Cryptography and Network Security Tutorial for Beginners with Examples
Cryptography
It is a science of converting a stream of text into coded form in such a way that that only the sender and receiver of the coded text can decode the text. Can decode the text.
Now a days, computer use requires automated tools to protect files and other stored information. Use of network and communication links require measure to protect data during transmission.
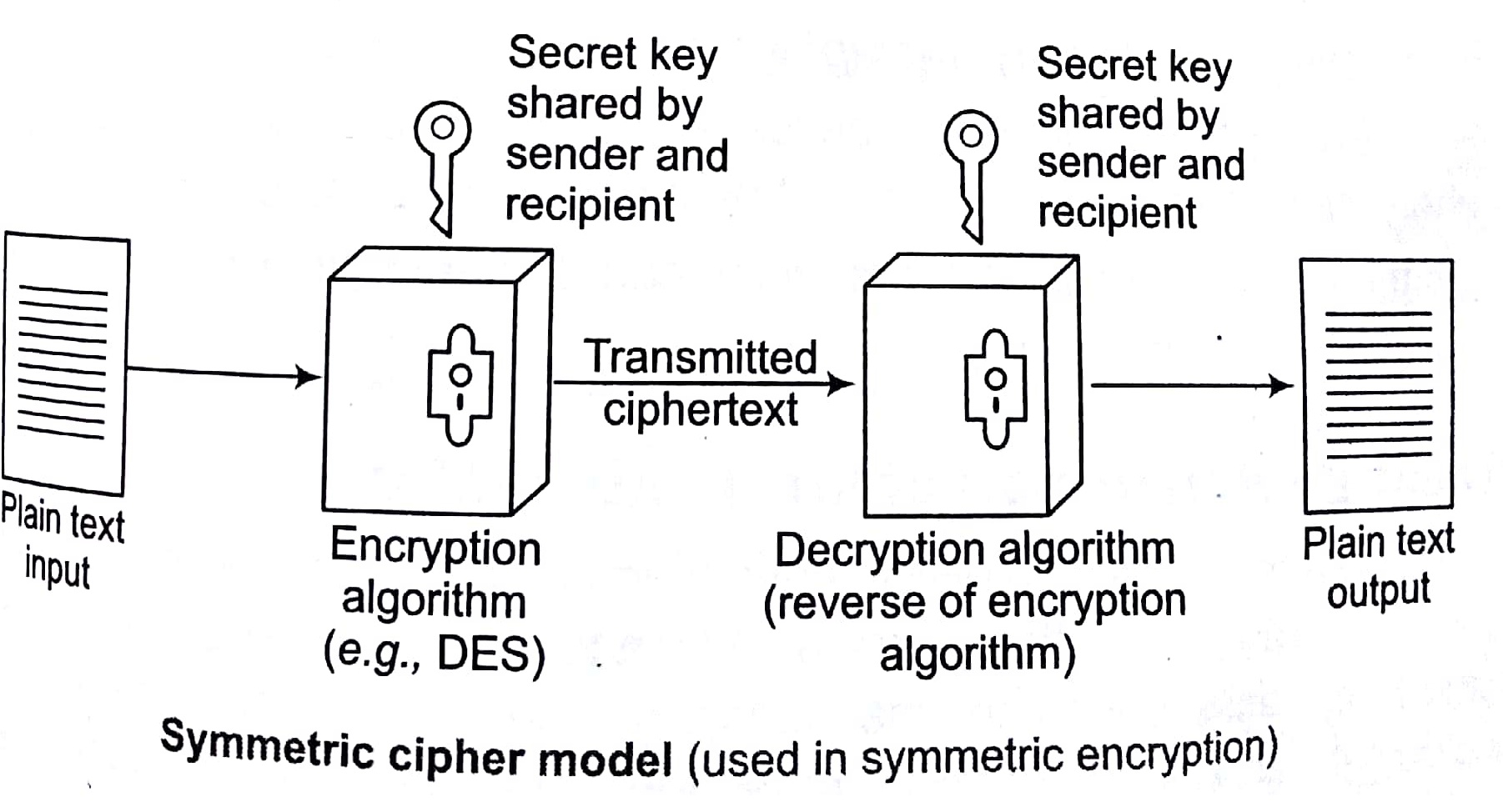
Symmetric/Private Key Cryptography (Conventional/ Private key/Single key)
Symmetric key algorithms are a class of algorithms for cryptography that use the same cryptographic key for both encryption of plain text and symmetric key decryption of cipher-text. The may be identical or there may be a simple transformation to go between the two keys.
In symmetric private key cryptography the following key features are involved
- Sender and recipient share a common key.
- It was only prior to invention of public key in 1970.
- If this shared key is disclosed to opponent, communications are
- Hence, does not protect sender form receiver forging a message and claiming is sent by user.
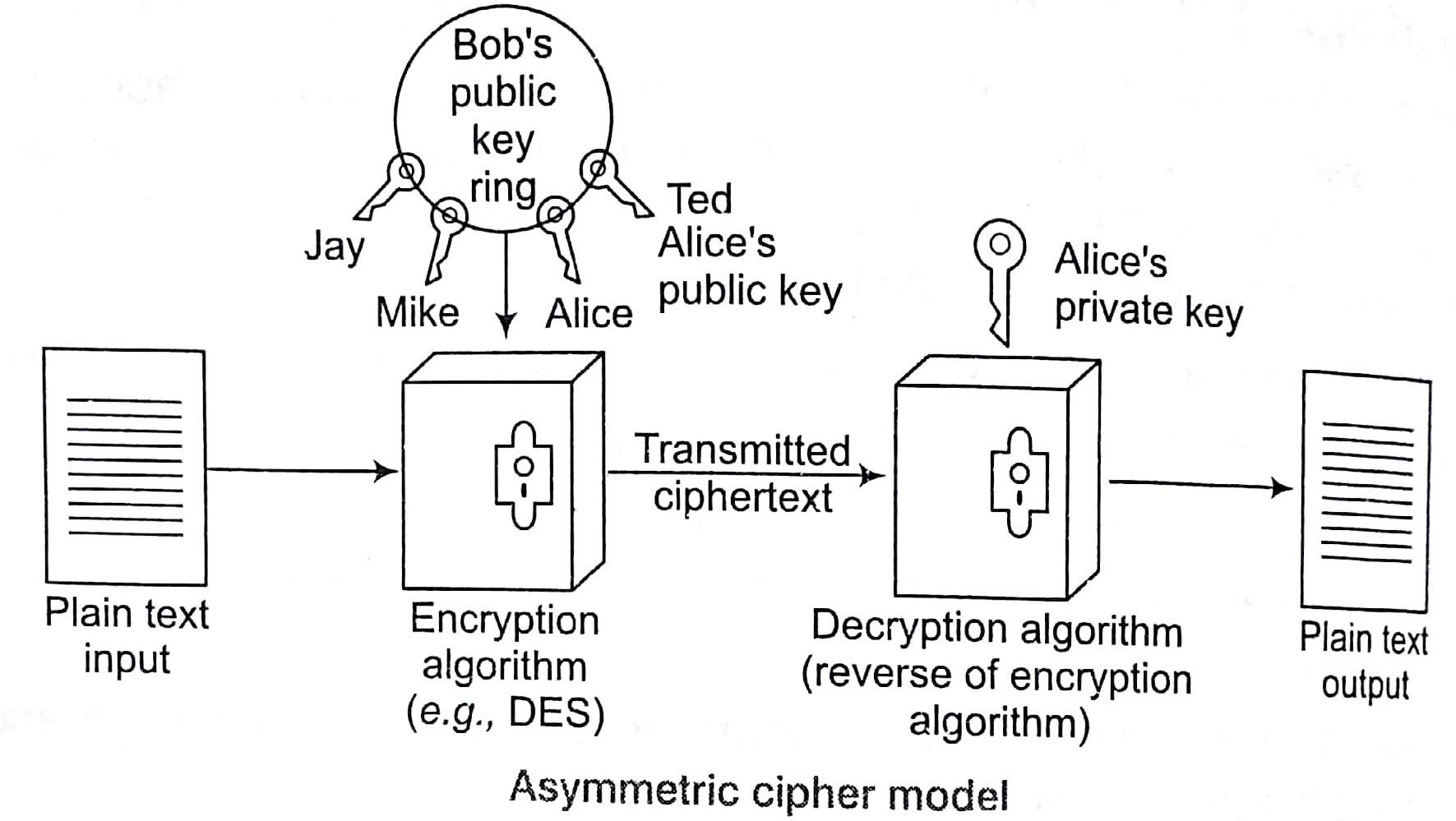
Asymmetric/Public Key Cryptography
A public key cryptography refers to cryptographic system requiring two separating keys, one of which is secrete/private and one of which is public although different, the two pats of the key pair are mathematically linked.
- Public Key: A public key, which may be known by anybody and used to encrypt messages and verify signatures.
- Private Key: A private key, known only to the recipient, used to decrypt messages and sign (create) signatures.
It is symmetric because those who encrypt messages or verify signature cannot decrypt messages or create signature it is computationally infeasible to find decryption key knowing only algorithm and encryption key.
Either of the two related keys can be used for encryption with the other used for decryption (in some schemes).
In the above public key cryptography mode
- Bob encrypts a plain-text message using Alice’s public key using encryption algorithm and sends it over communication channel.
- On the receiving end side, only Alice can decrypt this text as she only is having Alice’s private key.
Message Authentication Codes (MAC)
In cryptography, a Message Authentication Code (MAC) is a short piece of information used to authenticate a message and to provide integrity and authenticity assurance on the message. Integrity assurance detects accidental and international message changes, while authenticity assurance affirms the message’s origin.
A keyed function of a message sender of a message m computer MAC (m) and appends it to the message.
Verification: The receiver also computers MAC (m) and compares received value.
Security of MAC: An attacker should not be able to generate a valid (m, MAC(m)), even after seeing many valid messages MAC pairs, possible of his choice.
MAC form a Block Cipher
MAC from a block cipher can be obtained by using the following suggestions.
- Divide a massage into blocks.
- Computer a checksum by adding (or xoring) them.
- Encrypt the checksum.
Key Points
- MAC keys are symmetric. Hence, does not provide non-repudiation (unlike digital signatures).
- MAC function does not need to be invertiable.
- A MACed message is not necessarily encrypted.
Sorting in Design and Analysis of Algorithm Study Notes with Example
Learn Sorting in Handbook Series: Click here
Follow Us on Social Platforms to get Updated : twiter, facebook, Google Plus
