HTML Tutorial for Beginners Study Material Notes with Examples
HTML Tutorial for Beginners Study Material Notes with Examples:The Complete Guide of Computer Science and Information Technology to Crack any Examination:-In this cyberpoint9 tutorial we are going to describe about the concept of Any Competitive Examination in Computer Science and Information Technology and cyber programming. And also we will describe that how can we crack any Competitive Examination Like GATE-CS ,UGC-NET,BARC,VSSC, DRDO, ISRO, NASA, BHEL,SPACEX,GOOGLE,FACEBOOK, etc .This is the free Full Complete Guide for Computer Science and Information Technology Students and Achievers Scientist.In this tutorials: course for Beginners to Advance And why we use Handbook of CS AND IT to make more interactive and save our time for our Daily life. Best Online Tutorial for Computer Science and It students .When ever we want to learn any thing the things become more earlier is somebody/tutorial/study material taught us through Examples. Here we have tried to describe each and every concept of Programming and Cyber Security in the light of cyberpoint9.com best Hindi Short tutorial using simple and best possible example. These examples are so simple that even a beginner who had never even heard about hacking and Cyber law can easily learn and understand How the isro and barc drdo for computer science books works in our today’s Technical Field. This is the best tutorial/Study Material very beneficial for beginners as well as Professional.The Complete Guide of Computer Science and Information Technology.
HTML(Hyper Text Markup Language)
HTML is a method where ordinary text can be converted into hyper text. It is basic tools for designing a web page.
Hyper Text
A way of creating multimedia documents, also a method for providing links within the documents.
Markup Language
A method for embedding special tags that describe the structure as well as behaviour of a document.
HTML Tags
Developing a web page is concerned with
- Contents of the page • Appearance of the page
The appearance of the page is coded in HTML language, using HTML tags. An attribute of a tag is additional information
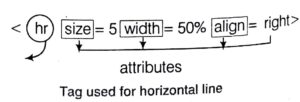
that is included inside the start tag.

Basic Structure of HTML Page
The HTML page can be saved as. html or .htm extension.
<HTML>
<HEAD>
//Head elements are to be written here
</HEAD>
< BODY >
//Body elements are to be written here
</BODY>
</HTML>
Here, the < > is called Starting Tag and < / > is called Closing Tag. The page will start with HTML tag, which will declare that , this page is an HTML page.
The HTML page is divided into two major parts.
- Head element 2. Body element
Head Element
Head element basically contains those tags which are useful to store some information about the current HTML page but they are not visible to web explorer. Some of head tags are also used to handle some events in HTML documents. Head elements are described as follows
<title> Tag
This tag is used to define title of the web page. The text that is written in between the opening and closing tags of title tag is visible at the topmost bar of web page.
<title> First web page </title>
<base > Tag
Base tag defines the default address or default target for all links on a page.
< html >
<head>
< base href= “http:/ /www.abc.com/myfolder“i> <base target = ” — blank”/>
</head>
<body>
<a href = “mypage.iltrill”> Click Here < /a>
</body>
</html>
Here, <a> </a> defines the link to another page. This tag is also known as Anchor Tag. When you click on Click Here, it will redirect You to the www.abc.com/myfolder/mypage. html.
The href element in the base tag defines a base URL for all relative, the page and the target element in base.tag defines the location where no open all links in a page.
Attributes of target are as follow
Target = “_blank” means open the link page to the new window.
Target = “_parent” means open the link into the same * frame.
Target = “_self” means open the link into the same * frame.
Target = ” top” means open the link into the top * frame.
* frame specified by frame name
<link> Tag
The <link> tag defines the relationship between a document and an external resource.
<head>
<link rel = “stylesheet” type = “text/css” href = “abc.css”/> </head>
Here, the link tag is used to define that an external css file, i.e., abc.css has to be used in this html page.
Key Points
The attributes in link element are as follows
- Rel :Specifies the relationship between the current document and the linked
- Type: Specifies the MIME type of the linked document.
- Href : Specifies the location of the linked document.
- Rev: Specifies the relationship between the linked document and the current
- Charset: Specifies the character encoding of the linked document.
<Meta>Tag
This provides metadata about the HTML document. Metadata will not be displayed on the page, but will be machine parsable. The <meta> tag always goes inside the <head> . The Metadata can be used by browsers (how to display content or reload page), search engines (keywords) or other web services.
< head >
< meta name = “description” content = “free tutorial s”/ >
< meta name = “keywords” content = “HTML, CSS , XML”/>
< meta name = “author” content = “Mohan”/>
< meta http_equi v = “Content Type” content = “text . html ; charset =ISO- 8859-1″/>
</head>
Here,
- Name: Provides a name for the information in the content attribute.
- Http_equiv: Provides an HTTP header for the information in the content attribute values for this, attributes are content type, content-style-type, expires, refresh, set_cookie.
- Content: Specifies the content of the meta information.
- Scheme: Specifies a scheme to be used to interpret the values of the content attribute.
<script> Tag
It is used to define client-side script, such as Java script. This script element either contains scripting statements or it points to an external script file through the src attribute.
<head>
<script type = “text/java script”>
document .write (“Hello World !”);
</script>
</head>
<style> Tag
Style tag is used to define style information for an HTML document. Inside the style element we specify how HTML elements should render in a browser.
<html >
<head>
<style type = “text/css”>
h1(color : red}
p (color :blue )
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Header 1</h1>
<p > A paragraph. </p>
</ body>
</html>
<body> Tag
The body tag contains all those text that is to be displayed in web tag. The tag inside the body tag are used to format the text written and images to be displayed in web page. It also helps to align the various objects in web page.
Key Points
- The only possible value is “text/css” for this tag.
- The style element always goes inside the head sections.
- The tag inside the body tag are used to format the text written and images to be displayed in web page.
- <body> Tag also helps to align the various objects in web page.
Text Formatting Tags
- <b>Tag b stands for Bold tag. The text written between <b> and </b> tag will be displayed as bold letters.
- <i>Tag i stands for italic format means the text written between <i> and </i> will be displayed as italic format.
- < big >Tag This tag helps the text to be displayed in bigger
- < small>Tag This tag renders a smaller text.
- <u> Tag The text written between <u> and </u> will be displayed as underlined text.
- <q> Tag This tag defines the short quotation. The text will be quoted, if we use this tags.
<html >
<body>
<q> Here comes a short quotation </q>
</body>
</html>
Output “Here comes a short quotation”
- <strong> Tag This tag is used to display the text in bold format.
- <sub> Tag This tag defines subscript text
e.g. ,
H <sub> 2 </sub> 0
Output H20
- <sup> Tag This tag is used to display superscripted text.
e g.
4<sup>th</sup>Edition
Output 4th Edition
- Headings <hl> …<h6> Tags The <h1> to <h6> tags are used to define HTML headings. <h1> defines the largest and <h 6 > defines the smallest heading.
- <font> Tag This tag is used to describe the font style of a text.
e.g.,
< font color = “red” size = “16” face = “arial” > This is my font tag test </font>
The color attribute defines the color of the text. The value in the color attribute can be given by directly by name or by specifying a particular hexadecimal 6 digit number like color = “#FFOEE2” or by RGB combination like color = “rgb(50, 50, 50)” size attribute defines the size of the text and the face attribute defines the font type of the text.
- <abbr> Tag The <abbr> tag describes an abbreviated phrase.
The <abbr> Tag
The <abbr title = “World Health Organisation”>WHO </abbr> was founded in 1948. Here, when we will move the mouse over WHO it will display
Output “World Health Organisation”
- <blockquote> Tag This tag defines a long quotation. A browser inserts white space before and after blockquote element. It also inserts margins for the blockquote element.
- <del> Tag The <del > tag is used to define the text that has been deleted from q document.
e.g., The leader of this class is <del> Rahul </del> Neha.
Output The leader of this class is Neha.
Text Alignment Tags
There are some tags that are used to align text into left, center, right or justified position.
These tags are described as follows
- <p>Tag This tag is used to define a new paragraph. The attributes in paragraph tag is align values of which is right, center, justified or left.
<p align= “left,” >
- <br> Tag This tag is used to start next line or line break The text written after < br> tag will be stated from next line
e.g., This is my first web page <br> And I learned everything about HTML. Output This is my first web page
And I learned everything about HTML.
Note that <br> tag has no Closing element.
(C) <pre> Tag As we know that without <br> tag line break is not applied to web page.
Thus, for every alignment corresponding tag is to be defined. <pre> tag eliminates this over head. The text written between <pre> tag is displayed in web page in the same manner as it is written in coding.
e.g.,
<pre>
Hi ! my name is Rahul and I love web technology. </pre>
Output
Hi ! my name is Rahul and
I love web technology.
(d) <center> Tag This tag is used to align a text to the center. This means the text that is written between center tag will be displayed on the center of page.
Lists
HTML supports three types of lists as follows
- Unordered List (Unnumbered or Buffeted List)
- Ordered List (Numbered List)
- Definition List
UnOrdered List
This defines the element using bullets.
<body>
<ul>
<li> Coffee </li >
<li>Milk</li>
<li> Bread </l i>
</ul>
</body>
Output
Coffee
Milk
Bread
Ordered List
In ordered list, elements are defined in ordered manner i.e., numbered.
e.g.,
<ol>
<li > Oranges </li>
<li> Peaches </li>
<li> Grapes </li>
</ol>
Output
- Oranges
- Peaches
- Grapes
Definition List
A definition list is a list of items, with a description of items. The <dl> tag defines a definition list . The <dl> tag is used in conjunction with <dt> (defines the item in the list) and <dd> (describes the item in the list). e.g.,
<dl>
<dt> CS </dt>
<dd> – Computer Science </dd>
<dt> IT</dt>
<dd>- Information Technology </dd>
</dl>
Output
Cs
–Computer Science
IT
–Information Technology
Tables
Tables are very useful for presentation of tabular information. For this purpose, we use <table> tag.
e.g.,
<table border = “5” >
<caption> <b> Student Record </b> </caption>
<tr>
<th> Roll No </th>
<th> Student Name </th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> 001 </td> <td> Ram </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> 002 </td> <td> Shyam </td>
</tr>
</table>
Output

Table Elements
Table elements are as follows
<table> </table> Defines a table in HTML.
<caption> </caption> Defines caption for the title of the table. Attribute Align = Both can be used to position the caption below the table.
<tr> </tr> Specifies a table row within a table.
<th> </th> Defines a table header cell. By default the text in this cell is bold and centered.
<td> </td> Defines the table data cell. By default the text in this cell is aligned left and centered vertically.
Some of the table attributes are described below
bgcolor This is used to define the background color in table.
bgorder This specifies width around the border. .
cellpadding Specifies the space between the cell wall and the cell content.
cellspacing Specifies the space between cells.
width Specifies the width of a table.
- align This attribute aligns the content of row in three manners e., left, right, center.
valign This attribute aligns the content of a cell in three values for this are middle, top and bottom.
image The <img> tag allows to display images on web page. Images are the binary representation of data in pixel form.
Inline image Image is inserted at a particular location “in a line” within a web page.
- syntax <img src = “myfolder/abc.jpg” height = “50%” width = “50%” alt = “mypics” border = “3” align = “center”›
Here, the src attribute defines the path of the image. Height defines the height of the image that can be given in form of % or pixel value a height = “100”. Similarly, width attribute defines the width of the image.
Key Points
- The alt attribute defines the alternate text that will he displayed, if the image is not visible.
- Border attribute defines the border width around the image.
- Align attribute defines the alignment of the image, values can he left, center, right, top, bottom.
Link
Links are used to jump from one html page to another html page. <a> anchor tag is used to create link between two html pages.
e.g., < a href = “myfolder/nextpage.html”> Click Here </a> when, we will cl!ck on the “Click Here” it will redirect the current page to nextpage.html.
HTML Form
Forms not only provide communication from user to server, but also provide powerful stuff and can add a lot of value to the web pages.
Forms are used to get inputs from the user. The user input is submitted to the server. A form is defined with
<form>……</form> tag.
Form tag has three attributes as follows
Action Attribute
This attribute specifies where to send the form-data when a form is submitted or what action needs to be performed when form is submitted.
e.g., If we want a program “\cgi\bin\comments.exe” to be executed, when a form is submitted , then we write
action = “/cgi/bin/comments.exe”
Method Attribute
This attribute defines how the data will be submitted to the server to go to the next page. Two methods are there, get and post. In get method, the data of the form is appended in the URL of next page.
e.g., <form method = “get/post” action = “a. exe” >
Encrypt Attribute
This is used to inform the server the way to handle the encryption process.
encrypt = “application/x-www. form-urlencoded”
Elements of a Form
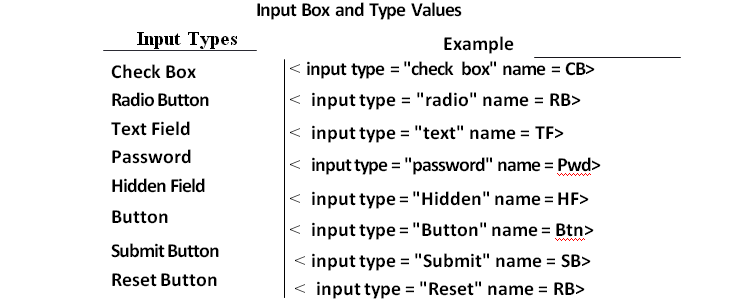
The elements of a form can be of three types
- Input box
- Selection list box or combo box
- Text area
Selection Box (Combo Box) The <select> • tag is used to create a select list (drop down list).
The option> tag inside the select element define the available options in the list.
e.g.
<select>
<option value = “volvo” > volvo < /option> <option value = “scoda” > scoda < /option>
<option value = “Mercedes” > mercedes </option</select>
Text Area Multiline area in which user can type the text as input. It has three attributes as number of rows, number of columns in text area and the name of the variable.
e.g.,
<html>
<body>
<center> Enter your text
<text area Name = “Remarks” rows = 5 column = 50>
</text area>
</center>
</body>
</html>
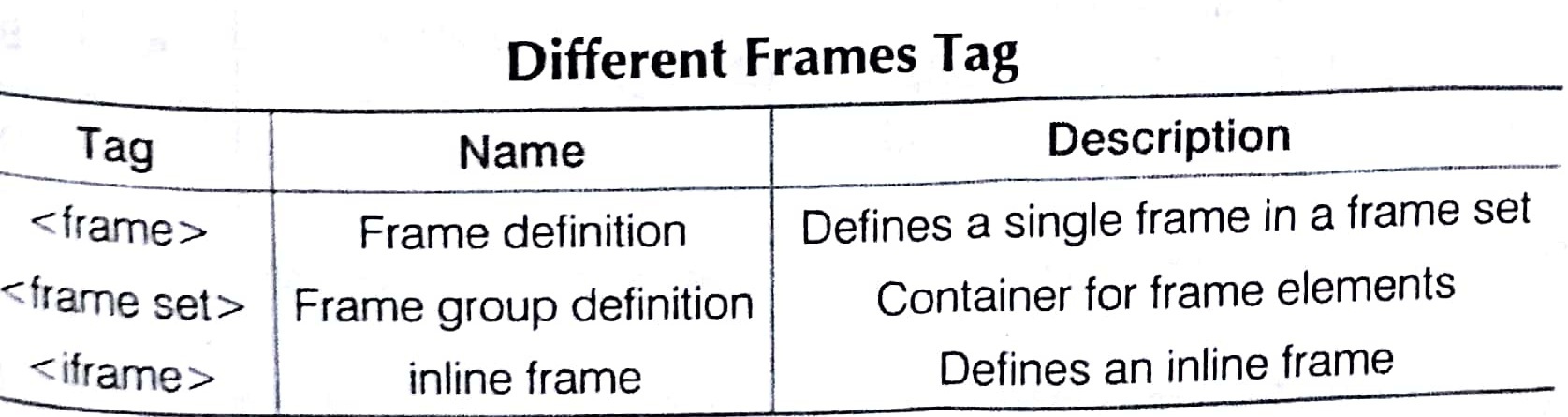
Frames
Frames allow us to divide a browser window into several independent Parts. It is a way of displaying two or more pages at once.
Frames could be applied for the following on the web page as given below
- To display the log or a stationary information in one fixed portion of the
- For the table of contents in a page, where people can just click and move around the website without having to more constantly to the contents
Example for Cols
< frameset cols = 200, 400> size is in pixel
cols specify the number of vertical windows or frames and values in them specify the width of the frame in frameset. We can provide values either in pixel or in percentage. For percentage we need to mention values with % sign, For pixel, we should not give any sign with the value as in above example.
Example for Rows
Row specifies number of horizontal windows or frames and values in rows specify the height of the frame
< frameset rows = 100, 40%, *›
Frame window will have three frames, where the height of the first frame is of 100 pixels, the second is 40% of the main window and the height of the 3rd one will occupy the rest of the window space.

e.g.,
<frameset rows = “50%”, “50%”>

<frame set col s = “50%”, “50%”>
<frame src = A. html>
<frame src = B. html> </frameset>
<frame cols = “50%”, “50%”>
<frame src = C. htmi >
<f rame src = D.htmt>
</ frameset>
XML Tutorial for Beginners Study Material Notes with Examples
XML Tutorial for Beginners Study Material Notes with Examples: Click here
Follow Us on Social Platforms to get Updated : twiter, facebook, Google Plus
